Infectious diseases are diseases whose development is associated with the entry of pathogenic organisms into the human body. Pathogens can include various bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa. They can affect virtually all systems of the human body, starting with the skin and mucous membranes, ending with the organs of the digestive, respiratory, genitourinary and even musculoskeletal systems. Infectious diseases still occupy a significant place in the structure of human morbidity and mortality, second only to diseases of the cardiovascular system and cancer.
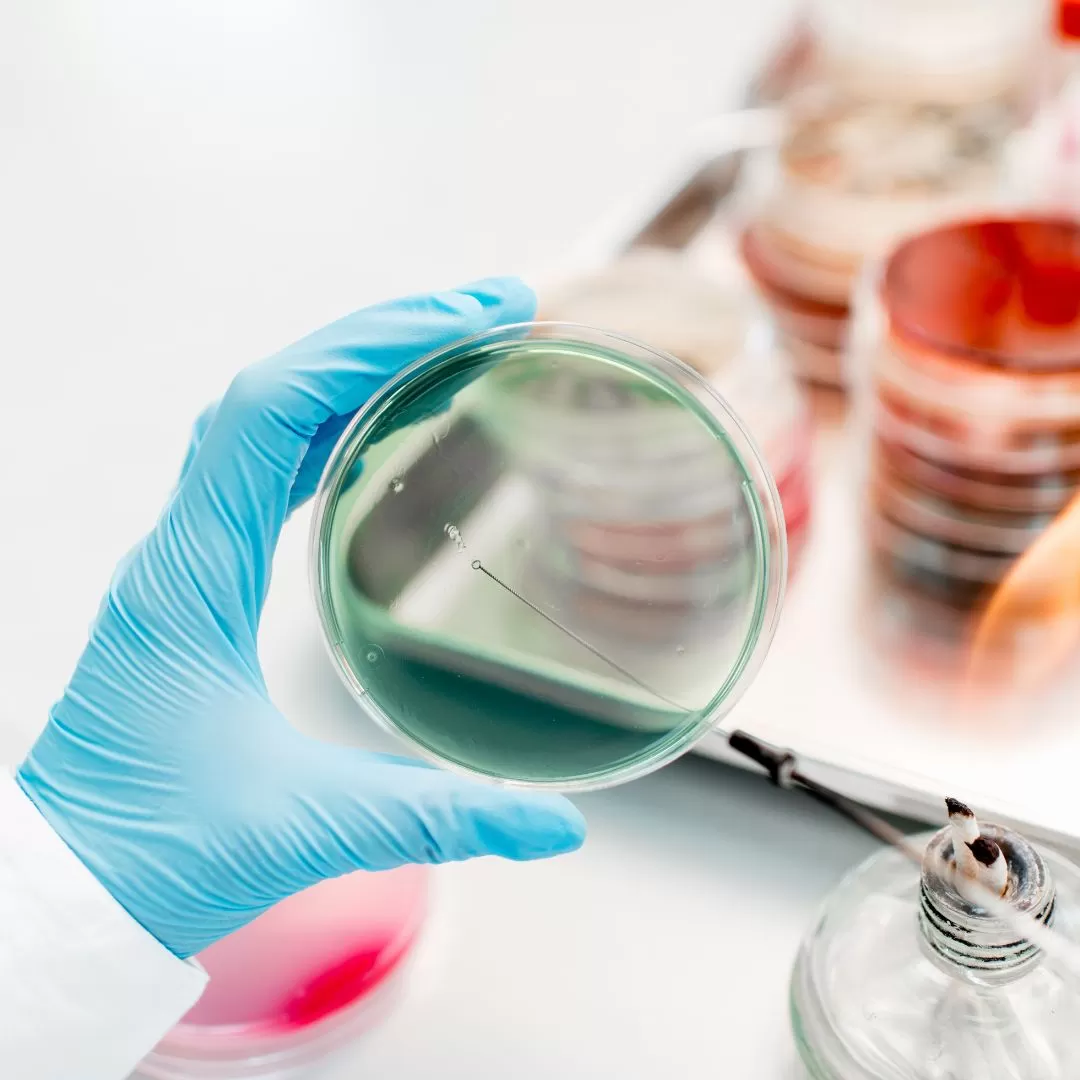
The essence of bacteriological studies is the sowing of any biomaterial (blood, urine, feces, etc.) on a nutrient medium, where optimal conditions for the growth of microorganisms are created. This is done in order to isolate a pure culture of the causative agent of the disease with the subsequent determination of its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. The results of bacteriological analysis contribute to the selection of the most effective drug for antibacterial therapy, timely implementation of measures to prevent nosocomial infections.
Indications for bacteriologic testing:
- chronic respiratory diseases
- purulent processes
- enteric infections
- urinary infections
- sexually transmitted diseases
- sepsis
Advantages of this research method:
- high specificity, which is essential in establishing the cause of the infectious process,
- it can be used to determine the properties of isolated microorganisms necessary for the correct prescription of therapy (antibacterial drugs, antimycotic drugs, etc.).
All of studies, performed in the bacteriological laboratory are performed on modern analyzers. The main disadvantage of bacteriological examination is its duration, which can be up to 14 days.