Pathology of the central zone of the fundus (macula, "yellow spot", central fossa) inevitably leads to a decrease in visual functions.
Among the acquired during the life of macular degeneration diseases, the following are distinguished:
Age-related macular dystrophy
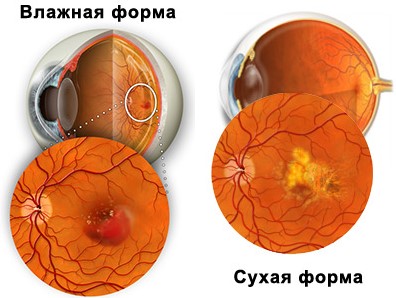 - a group of diseases with progressive changes in the retina in the central parts of the eye.
- a group of diseases with progressive changes in the retina in the central parts of the eye. There are "dry" and "wet" forms of the disease, the methods of treatment of which are diametrically opposed;
Central serous chorioretinopathy
- pathology of the "yellow spot" area due to detachment of the pigment and / or neuroepithelium. Occurring more often at a young age, the disease requires urgent treatment in order to restore vision;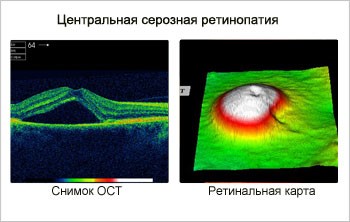
Myopic maculopathy
- severe complication of pathological myopia, threatening loss of central vision. Early treatment can prevent "central" blindness;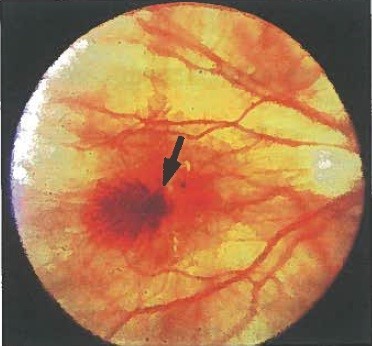
Senile macular breakage
- rupture of the photosensory membrane of the eye in the macula due to the traction effect of altered structures. Even a complete neuroepithelial defect taken for treatment on time can be closed with the restoration of visual functions;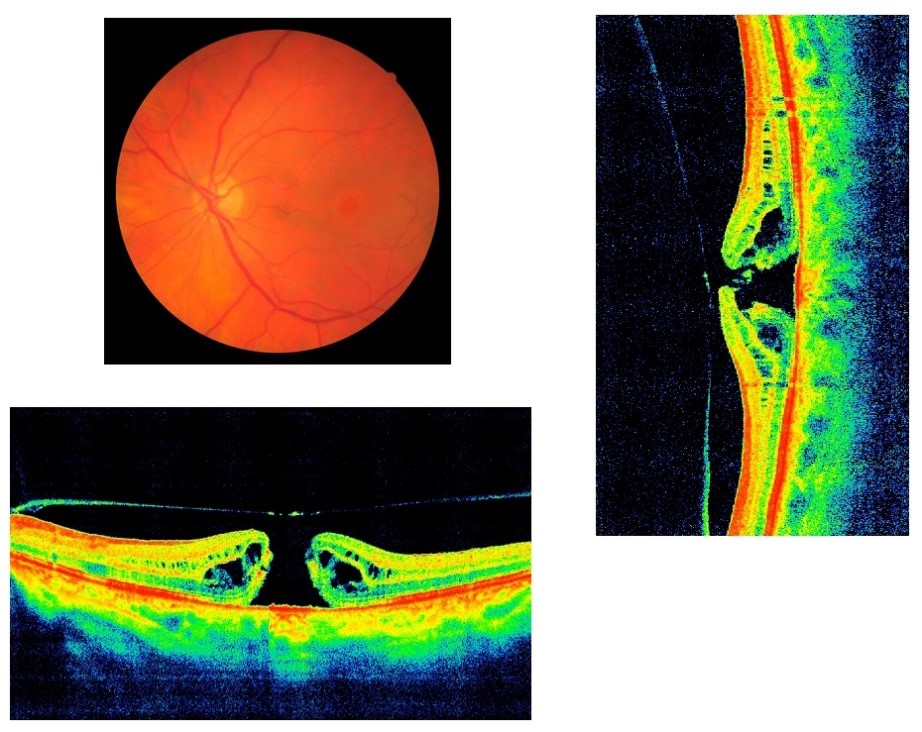
Cystic macular edema
- accumulation of fluid in the form of cysts in the outer plexiform layer of the neuroepithelium as a result of various reasons (complication of surgical eye treatment, diabetic changes, etc.). Difficulties in treatment require the fastest possible initiation of therapy and a thorough systemic approach. Sometimes you have to fight with macular edema for years, while maintaining vision;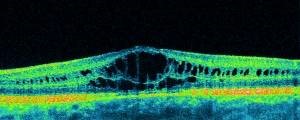
Medicinal maculopathies
- changes in the area of "yellow spot" of the fundus as a result of taking medications;Post-traumatic macular degeneration
- in addition to a direct penetrating wound of this area of the fundus, changes can occur with any contusion damage not only to the eye, but also to the head and torso. A common cause of the disease is wave damage to the unprotected eye by ultraviolet rays (tanning, solariums), as well as infrared radiation (solar eclipse, blast furnaces, etc.). With a sharp compression of the chest or abdominal cavity, as well as a sharp displacement, which is typical for traffic accidents and emergencies, Valsalva maculopathy occurs;Other varieties of rare maculopathies
- anginoid streaks, choroidal folds, etc.What you need to pay attention to
CLINICAL ASPECTS
With the pathology of the central fovea of the fundus, the patient makes characteristic complaints about:
 1. Decrement in visual acuity. Using both eyes for vision, sometimes people do not immediately notice the deterioration in vision in one eye. Therefore, ophthalmologists recommend occasionally, covering the eyes in turn, to compare the visual acuity of each eye (for those using the correction, the procedure is carried out in glasses or contact lenses);
1. Decrement in visual acuity. Using both eyes for vision, sometimes people do not immediately notice the deterioration in vision in one eye. Therefore, ophthalmologists recommend occasionally, covering the eyes in turn, to compare the visual acuity of each eye (for those using the correction, the procedure is carried out in glasses or contact lenses);
 2. All patients with macular degeneration note changes in the visual field to one degree or another. Before the eyes appear "zones of blindness" of varying degrees of severity. This condition is characterized by the appearance of a “positive” scotoma, in which the patient complains of the appearance of a “spot before the eye”;
2. All patients with macular degeneration note changes in the visual field to one degree or another. Before the eyes appear "zones of blindness" of varying degrees of severity. This condition is characterized by the appearance of a “positive” scotoma, in which the patient complains of the appearance of a “spot before the eye”;
 3. Changes in color perception. In some forms of macular degeneration, there is a difference in the perception of green and red in each eye separately;
3. Changes in color perception. In some forms of macular degeneration, there is a difference in the perception of green and red in each eye separately;
4. Metamorphopsia - a frequent complaint of patients with macular degeneration. Objects in the field of view may be perceived as distorted, lines broken. Sometimes the details of the surrounding world in front of the affected eye are reduced in size (micropsia) or enlarged (macropsia).

IF ANY OF THESE CONDITIONS APPEAR, YOU NEED TO SEE A DOCTOR IMMEDIATELY!
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF MACULODYSTROPHIC DISEASES IN RCMC
Given the multiple causes of the pathology of the macular area of the fundus, the diagnostic search for the underlying disease can be difficult. A thorough and comprehensive examination is necessary for the correct and most effective treatment.
DIAGNOSTIC MEASURES
Visual acuity test.
In the pathology of the macula, visual impairment is characteristic.
A functional study of the nature of vision in the central region using the Amsler grid
was developed by the Swiss professor of ophthalmology Mark Amsler (1891-1968) and has been widely used since 1945. The Amsler grid is a square lattice with 192 equal cells, in the middle of which there is a bold dot.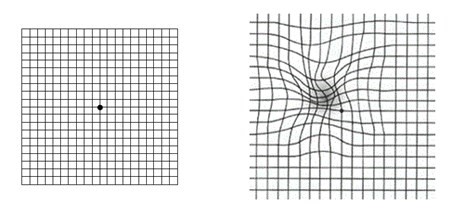
Performing the Amsler Grid Test
- Place so that the distance from the grill to the eyes is equal to the length of the outstretched arm.
- If you normally wear glasses or contact lenses, you should now have them on. You should be able to see the grid well.
- Cover one eye with your hand or piece of paper.
- With the other eye, look at the dot in the middle of the grid. Look at it for 3-5 seconds, then begin to gradually approach the table, while not taking your eyes off the point in the middle, until you reach a distance of about 20 cm.
- Do the same with the second eye.
If during the test all lines of the Amsler grid were smooth and continuous, then no signs of pathologies in the central region of the retina (macula) were detected. Otherwise, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
Perimetry
Examination of the patient's visual field is important not only for determining the localization of scotomas (visual field defects), but also for dynamic monitoring in order to assess the effectiveness of treatment. Computer static perimetry is the most objective and informative. The study allows not only to identify defects in the field of view, but also to control their parameters during treatment.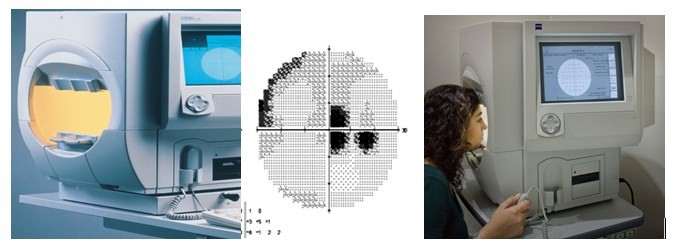
MICROPERIMETRY
by the first and only fundus microperimeter MAIA (CenterVue, Италия). The study allows to identify the localization of visual field defects, correlating them with the anatomy of the macular area, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and intensify therapeutic measures in time, up to surgical intervention.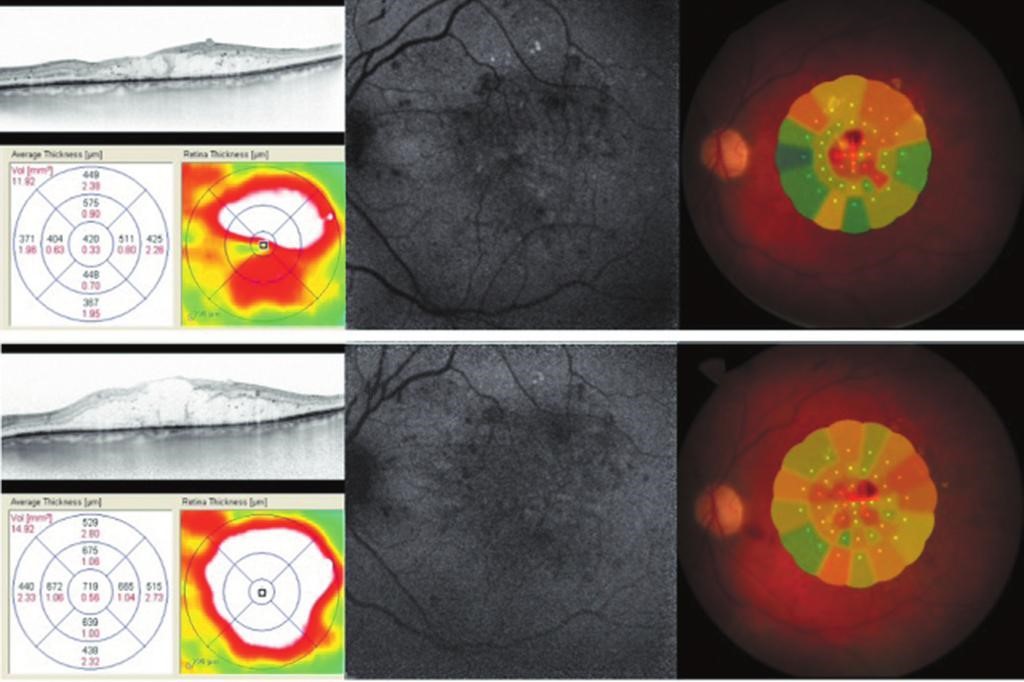
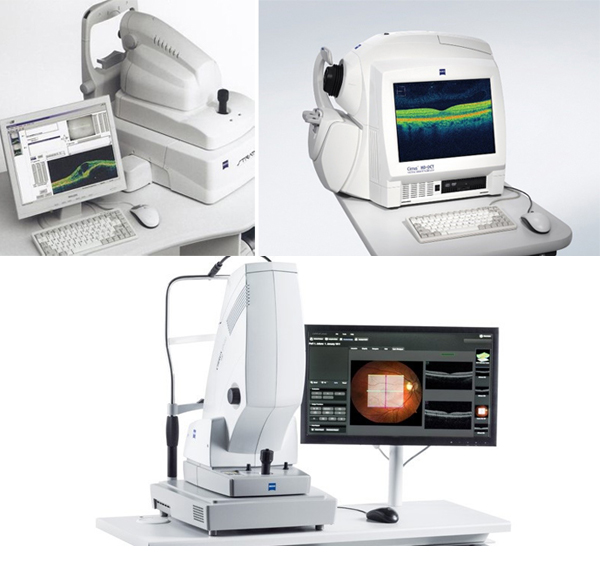
Optical coherence tomography of the retina in the central zone (ОCТ)
allows us to visualize changes in the structure of the retina with dimensions of micrometers. A feature of this diagnostic method is the ability to quantify the degree of changes and compare the results of several studies.In our Center ОCТ is carried out not only by two-dimensional mode on the device Stratus-3000 (Carl Zeiss, Germany), but also by three-dimensional mode on the only ones in the Republic of Belarus Cirrus™ HD-OCT model 5000 and CIRRUS photo 800 (Carl Zeiss, Germany).

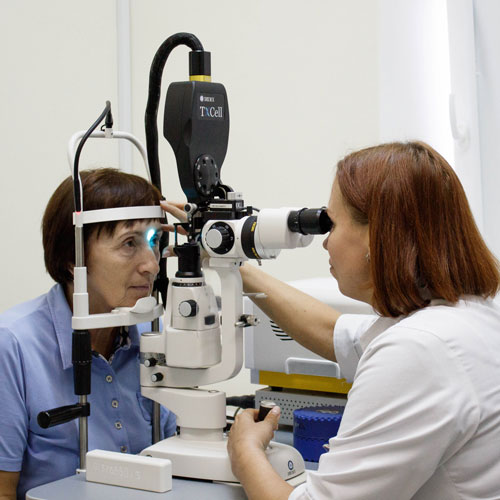
Fundus examination with a fundus lens
allows the ophthalmologist to examine in detail under magnification changes in the macular zone, determine the nature of the pathological process and plan treatment.
In our Center, slit lamps are equipped with cameras for photo and video recording of the condition of the fundus with the ability to compare images taken at different times and with different devices;

Fundus fluorescein angiography
is the only way of visual visualization of retinal vessels, which allows to identify pathological areas of newly formed vessels, as well as to determine leakage points in the eye membranes with an active release of a diagnostic dye. The choice of therapeutic or surgical treatment of fundus pathology based on fluorescein angiography data allows the ophthalmologist to obtain the maximum possible positive result in the treatment of the patient. Examination before and after treatment also makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of measures and make changes in the tactics of patient management.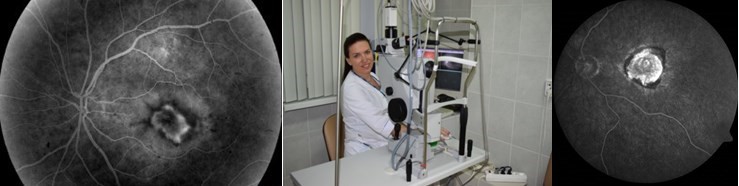
THERAPEUTIC MEASURES
Difficulties in the treatment of pathology of the macular area lie in the high functional significance of this area of the fundus. The fovea is a cluster of highly sensitive photosensory nerve cells.
To save the maximum possible number of neurons and eliminate the pathological process is a difficult task for a retinologist. Among the methods of treatment have proven:
Therapeutic regular courses of neurotrophic therapy
give a good result in maintaining the functional state of retinal and optic nerve neurons. In addition to taking oral drugs in the form of tablets or capsules, intramuscular and intravenous administration of morsulus is recommended. The maximum effect is obtained from retrobulbar and parabulbar injections, as well as the introduction of the drug into the sub-Tenon space directly to the posterior pole of the eyeball.Laser treatment of macular pathology
in some conditions is a quick and effective way to solve the problem. However, in other cases, treatment with laser radiation is strictly contraindicated. It is possible to determine the possibility of laser therapy only after a thorough examination. Surgical treatment of macular pathology in our Center is carried out using a multiwave laser VISULAS Trion (Carl Zeiss, Germany), as well as laser IQ 577 (Iridex, USA) using a “yellow” laser loyal to photoreceptors and sparing technology MicroPulse.The surgical method of treatment
is carried out with fibrotic changes in the intraocular structures and consists in the removal of newly formed membranes. This method weakens the tension of the retina and prevents the appearance of ruptures of the neuroepithelium. Vitreo-retinal surgery for macular breakage has also proven itself well.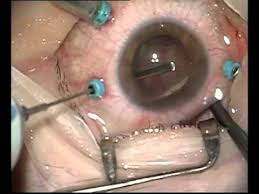
Intravitreal (intraocular) injections.
Treatment with angiogenesis inhibitors - anti-VEGF therapy - in recent years is increasingly the first and only method, especially in the presence of edema and retinal neovascularization. Our Center uses only approved in the Republic of Belarus for use in & nbsp; ophthalmology preparations (Eylea, Lucentis)!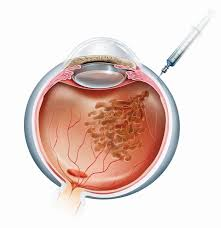
The medicine is injected directly into the eye in an operating room. The introduction of drugs is carried out by ophthalmologists-surgeons with the highest category.
The course of treatment always begins with three loading injections with an interval of 1 month (for diabetic macular edema - from five). Subsequently, for complete stabilization of the process, treatment is continued at intervals of 2 or more months.
Treatment of common diseases (arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, etc.) should not be interrupted! In the evening before the procedure and in the morning on the day of the procedure, it is necessary to control blood pressure.
Our Center performs a full range of diagnostics of central vision pathology, as well as possible treatment.
AFTER EXAMINATION OF THE PATIENT, THE OPHTHALMOLOGIST DEVELOPS AN INDIVIDUAL TREATMENT PROGRAM.
You have the possibility of examination and treatment in our department and on a paid basis.
Reception is conducted by doctors of the highest category.
The most modern equipment and the best specialists will help in solving vision problems!
PREPARATION FOR DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PROCEDURES
- do not wear soft contact lenses before the examination, preferably 5-7 days
- bring your ophthalmologist's examination data with you (if any)
- bring with you: passport, sunglasses, handkerchief
- do not drive for 4-5 hours after the examination
- be without makeup
In each individual case, preparation for diagnostics and treatment procedures is negotiated individually.
HOW TO GET TO THE TREATMENT OF MACULODYSTROPHIC DISEASES IN RCMC
- Call the Contact Center to make an appointment
- Conclude an agreement for the provision of paid services at the reception
- Pay the bill at the cash desk of the RCMC or through ERIP for the initial appointment with an ophthalmologist (all additional examinations are paid separately after the appointment)
- Arrive at the appointment on time.