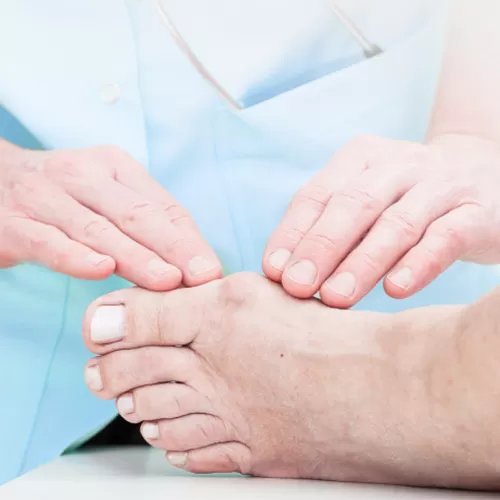
Gout is a chronic condition associated with a disturbance in uric acid metabolism. Gout affects 1-2% of the population and represents a type of inflammatory joint process.
Symptoms and Signs:
- Joint pain. Unpleasant sensations most commonly appear in the big toe, although gout can affect any other joints. Pain attacks last for several hours and are followed by periods of relief;
- Discomfort related to joint swelling. This symptom can last for several days or weeks;
- Redness of the skin around the joint. The affected joint feels warm to the touch;
- Impaired mobility of the affected limb;
- Migrating pain, where different joints can bother the patient throughout the day;
- Deformation of joints and bones;
- Appearance of subcutaneous nodules (tophi) in various areas of the body.
As the disease progresses, signs of kidney disorders may occur, including painful urination, lower back pain, and the presence of blood in the urine.
Possible causes of gout:
- Genetic disorders. Certain genes inherited from parents are responsible for uric acid metabolism in the body. Genetic mutations can lead to elevated levels of this substance in the body;
- Kidney diseases affecting organ function. This is often chronic inflammation, infection, or congenital functional disorders;
- Various blood disorders that manifest as lipid imbalances and anemia;
- Chronic autoimmune skin disease (psoriasis);
- Uncontrolled intake of aspirin, diuretics, vitamin B3 supplements, ACE inhibitors, and other medications.
The exact causes of gout are unknown to doctors, but studying risk factors allows for disease prevention.
⠀
The diagnosis of gout is based on symptoms, including acute joint pain, redness, and swelling of the skin in the joint area. If necessary, a consultation with a nephrologist or urologist is appointed to assess kidney function. A final diagnosis is established after undergoing instrumental and laboratory studies. ⠀
⠀
The treatment of gout aims to alleviate pain and inflammation, as well as to manage the level of uric acid. Medications and diet can help control symptoms and prevent attacks.⠀
⠀
Proper nutrition is of great importance: limiting the consumption of meat, alcohol, and purine-rich foods can help reduce the risk of gout attacks.⠀
⠀
Physical activity and maintaining a normal body weight also contribute to improvement in the condition.⠀
⠀
Remember that for an accurate diagnosis and treatment, it is necessary to consult a rheumatologist. Take care of yourself and monitor your health!