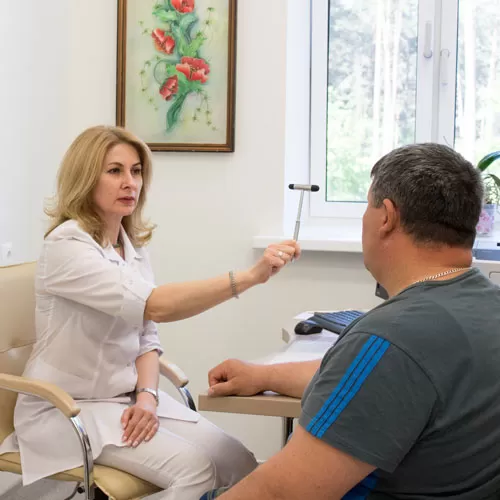
Dorsalgia is the collective term which is translated from Latin as “neck pain”. The term includes all the disorders of the spinal column that are mainly characterized by pain in any part of the back and spine. This condition is very widespread, and may occur in persons of any age.
INDICATIONS TO EXAMINATION AND TREATMENT
Symptoms of dorsalgia are varied:
- painful sensations in the back and spine ranging from spot to widespread pains. Intensity -- from light to very intensive pain, which may even impair a persons working capacity. Nature of pain -- dull, acute, throbbing, persistent or intermittent, nagging. Pain may develop after a physical load or at rest, and may be stabbing, disabling, etc.
- Postural disorders, gait abnormalities, numbness, leg discomfort;
- Headache, dizziness, general weakness.
Here is some additional information about dorsalgia

There is a number of predisposing factors that may aggravate the risk and may result in the development of dorsalgia:
- Spinal cord injuries (fractures, bruises, dislocations);
- Prolonged stay in an uncomfortable or improper position;
- Excessive spinal loads;
- Sudden temperature changes;
- Hypothermia;
- Frequent stresses and adverse emotions;
- Prolonged malnutrition;
- Alcoholism;
- Deficiency of physical exercises and weakness of the spinal muscle support structure.
- Some of medical diagnoses that may cause dorsalgia are: radiculitis, osteochondrosis, Bechterew disease, dislocation of spinal bones; invertebral disc protrusion; spinal disc herniation; spondylosis; incomplete dislocations; scoliosis.

In terms of localization, four types of dorsalgia are distinguished:
- Cervicalgia -- pain localized at the cervical spine;
- Thoracalgia (intercostal neuralgia) -- pain localized at the thoracic spine;
- Lumbalgia -- pain localized at the lumbar spine;
- Combined dorsalgia -- pain localized in two or three regions of spine.
In terms of its origin, dorsalgia may either be:
- Vertebrogenic dorsalgia, when spine pain is caused by spinal disorders. This type includes:
- traumatic dorsalgia caused by spinal injuries;
- inflammatory dorsalgia, which is caused by inflammatory processes in the spinal cord;
- degenerative dorsalgia caused by degenerative processes in the spinal cord;
- neoplastic dorsalgina, which may be caused by a tumorous growth within the spine and its structures. And:
- Vertebrogenic dorsalgia, when spine pain is not caused by any spinal disorder. This includes:
- myofascial dorsalgia which is caused by changes in the spinal muscle support structure (sprains, bruises, inflammations, etc.);
- psychogenic dorsalgia which has no physical roots, and is caused by psychic or psychological factors;
- as well as other factors.
DIAGNOSTICS AND TREATMENT OF DORSALGIA AT THE RCMC
At our Center, we apply a comprehensive approach to the examination and diagnosis of dorsalgia in each individual case.
The Neurology Department of the Center performs:
- Interview (history taking and collection of information on the patient’s complaints). This makes it possible to find out the patient's complaints, their history, and to clarify the genesis of the underlying disease, its complications and its causes;
- Examination. This allows us to reveal forced positions of the body, visible defects of the spine, abnormalities of active and passive movements at the affected section of the spine, etc.
- Palpation. Examination of the spine by touch helps to reveal strains of the muscular support structure of the spine, deformations, etc.
- Neurological examination. A test of skin and muscle fiber sensitivity (to pain, temperature and tactile sensations), persistence of physiologic reflexes, palsy or paralysis, presence of any pathological reflexes.
- Vertebral X-ray imaging in two projections (antero-posterior and lateral). This makes it possible to reveal spinal column deformations, the status of the spinal canal, any fractures, dislocations and other changes of bone tissue.
- CT (computer tomography). Layer-by-layer X-ray images enable physicians to reveal the pathologic area with high precision, as well as to detect loss of integrity not only of the spine but also of the spinal cord, etc.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). This technique offers the most accurate results. It makes it possible to reveal any abnormalitiesd of the spinal structure, the spinal cord, soft tissues, vessels and nerves.
- Cerebro-spinal puncture. This technique makes it possible to identify a hematomyelia, the presence of tumor cells in the cerebrospinal fluid, occurrence of inflammatory processes, etc.
- Myelography. This contrast X-ray image helps to determine the condition of the spinal cord.
- Scintigraphy allows to identify focal changes in tissues in order to verify oncological or infectious diseases.
- Electro-neuro-myography makes it possible to detect nerve fiber conduction abnormalities, and is often used for ongoing monitoring of disease progress and therapy effectiveness.
- Laboratory analysis is used when it is necessary to verify inflammatory, oncological and infectious processes.
Our Center performs comprehensive treatment of dorsalgia
Treatment of dorsalgia of any localization and origin may be divided into conservative (pharmaceutical and non-drug) and operative treatment.
Pharmaceutical treatment involves application of a broad spectrum of pharmaceuticals that may be administered intravenously, intramuscularly or orally.
Blocks using local anesthetic and steroid agents (blockage of trigger point areas or paravertebral blocks).

Non-drug therapy techniques are employed after the abatement of acute manifestations of dorsalgia when the painful syndrome is less pronounced. These methods include physiotherapy:
- needle therapy;
- spinal traction (including underwater traction);
- laser therapy;
- physical therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- osteopathy;
- electrophoresis;
- massage;
- hydrotherapy;
- mud therapy;
- swimming;
- manipulative therapy.
Operative therapy is appointed in exceptional cases after conservative therapy proved ineffective.
HOW TO GET TREATMENT AT THE RCMC
- Call the Contact Center to make an appointment
- Conclude a contract for the provision of paid services at the registry
- Pay the invoice at the cash desk of the RCMC or via ЕРИП (SSIS: Single Settlement and Information Space)
- Come to the consultation on time.